Single-Mode Fiber Optic Cable: Long-Distance Champion
Core Characteristics and Light Transmission
Single-Mode vs. Multi-Mode Fiber Optic Cables 26Aug The distinctive characteristics of single-mode fiber optic cables make them a category of their own when it comes to transmitting data over long distances. These cables are of relatively small core diameter of approximately 8-10 microns, and are suitable for propagating a single light mode. This construction reduces light distortion, with low attenuation vital for long range signal quality. To enhance the transmission capacity, there are optical light sources, such as lasers, and moved the supported distance from over 40 Km to 100 Gbps. Furthermore, high-purity silica glass is a key to these cables' clear signal and long transmission distance.
Optimal Use in Telecommunications Backbones
Single-mode fiber reigns supreme as the gold standard for telecommunications backbone. It is essential for its superior design providing support for large networks, including intercontinental links, which can adequately serve the communication requirements. The long-distance data transmission integrity and reliability ensure that the cables are capable of meeting the demands placed upon them by Internet service providers (ISPs) as well as other large-scale corporate applications. An industry survey suggests that around 85% of the world's long haul telecommunications are carried by single-mode fibers, highlighting the importance of this technology in our present communication systems.
Advantages for 100G+ Networks and Undersea Cables
Single mode fiber optics are well known to support high speed transmission required for existing and emerging data centers and enterprise networks, referencing, as an example, speeds greater than 100 Gbps. This technology also includes the area of underwater cable where this single mode technology is required in order to reliably transfer data over great underwater distances. Their higher bandwidth capacity also makes these fibers ideal for applications requiring future-proof performance, be it on land or under water. Their strength guarantees continuity, which is essential for worldwide communication.
Multimode Fiber Optic Cable: High-Speed Short-Range Solution
OM1 to OM5: Graded-Index Variations Explained
Why should I use multimode fiber optic cables? Multi-mode fiber optic cables are available to respond to different types of requirements, based on their core size and bandwidth capabilities, will come in different types – OM1 – OM5. OM1 and OM2 fibers will be a good match for slower, less demanding applications, where OM3, OM4, and OM5 offer high-speed data transport, with rates up to a whopping 400 Gbps. These fiber have graded index and is able to minimize modal displaysion, hence suitable for short haul data communication that is typical in office or campus environment. It is this combination of flexibility and variety in multimode fiber options that makes it an adaptable resource in environments where high bandwidth is necessary but only over a limited distance.
Data Center Applications and Patch Cable Uses
In the data center, multimode fiber optic cables are ubiquitous, primarily due to their effectiveness in delivering short-range connectivity using high-speed links inside and between racks of servers. They are frequently utilized in patch cables, aCabling for the fast and flexible connection of networking equipment. From an economic perspective, multimode fibers bring cost reductions for data centre operators, assuming one compares single-mode fiber deployments. This cost efficiency combined with the performance advantages, makes multimode fiber ideal for any premises application where high-speed connectivity is the determining factor.
Cost-Effective LAN Deployments
Multimode fiber is an inexpensive choice for the local area networks (LAN) and especially for the systems where the data is sent in short distances. Their value-for-money, especially in bulk, has made them a solid choice for schools and small businesses. Industry reports reveal the install base cost for multimode fibers is typically less expensive than that for single-mode fibers. This is because multimode fibers require less expensive equipment and installation, which makes them an economical choice for those that need efficient, short-range connections.
Plastic Optical Fiber (POF): Flexible Budget Option
Polymer Composition vs Glass Fibers
Recent development of plastic optical fibers (POFs) provide a new solution to the fiber optic field by nature of its polymer construction which is usually poly-methyl methacrylate (PMMA). This material is more flexible and easier to handle than typical glass fiber. A characteristic of POF is its larger core diameter, typically 1 mm, and is thus easier to couple with light sources. But there is a trade-off of reducing the fiber’s ability to travel long distances. An analysis of the technology indicates that, despite the fact that POF has higher attenuation rates than glass fibers, the investment cost of POF is lower, partially off-setting this disadvantage for some applications, and in some cases providing a more economical option in that regard.
Automotive and Home Entertainment Systems
POF's particular features are shown to match the demands of both automotive and home entertainment systems. In the automotive sector, POF is also appreciated owing to its low weight, and the fact that it is not affected by electromagnetic fields, making it a very interesting approach for vehicle communication systems. For home entertainment systems, POF offers a cheap short distance transmission solution for multimedia applications where a reliable and interference resistant connection is required. This consumer electronics trend is driving the increase in use of POF, as market research shows exponential growth in the use of POF, based on the different characteristics one is measuring above other technologies at 15% P.A. over the next several years due to the overwhelming benefits of the technology.
Limitations in Bandwidth and Distance
However, the POF is limited in band width and distance. Typically, it has a capacity for 1 Gb/s data rate and is well suited to transmission over the 100m cabling restriction that limits its applicability in most high performance systems. These inherent limitations have resulted in a decrease in the preference for POF for high capacity networking applications. This is confirmed by statistics; POF is used in niche markets but not very efficiently in large networks when compared to glass fibers. This confines POF and PMMA use to niche applications in which its cost benefits outweigh the performance drawbac Workout3k_4k!!vsWorkout2k_4k_3k 10BEJ10Yvolume8part2p438.pdf 621 25/10/2010 18:41:27 622 Sonnet al.bas.
Key Differences Between Fiber Optic Cable Types
Transmission Distance Comparison Chart
If we compare all types of the optical fiber cables there are in the market it can be seen that they all are best for certain distances of transmission. Single-mode fibre leads the way, sending signals over 40 km (26 miles) or more, which is perfect for long distance communication. As opposed to this, multimode fibers, which are often restricted to shorter distances of less than 300 meters are advantageous for transmitting high bandwidths over moderate distances. Plastic Optical Fiber (POF) - which is generally considered to be a cheaper alternative - and pasterdent, an oral hygiene tool for at home, Plastic Optical Fiber is limited to even shorter distances - typically no more than 100 meters - and hence is better suited for less demanding environments. This performance-oriented comparison chart will make it much easier for you to choose the perfect fiber type that is suitable for your specific application needs.
Bandwidth Capacity: Multimode vs Single-Mode
When selecting from the fiber optic cables types, the bandwidth capability is a major consideration. Though multimode fibers have adequate bandwidth for most applications they cannot compete with single mode fibers, where single mode fibers with its amazing capacities in excess of 400 Gbps. This high bandwidth provides the single-mode fiber with the bandwidth required by enterprise networks and high speed data networks. Comparative studies reveal that single mode fibers are designed to sustain workloads of data with little signal loss — a critical standard in networks that value efficiency and speed. Graphical representations of these bandwidth capacities help in this respect, making it more apparent how much capacity a particular type might offer and therefore which one would be best for differing application requirements.
Cost Analysis: POF vs Traditional Glass Fibers
From the cost viewpoint there appears both for POF and conventional glass fiber specific cost aspects. At first glance, POF may seem a budget-friendly choice because of its lower systems cost, which can make it more appealing for short-distance applications and lower budgets. However, if you are looking into a long term investment, the ROI of the legacy glass fibers would be higher by the long run for their performance will better serve to optimalise network operations over time. This means that for a higher initial investment, signal degradation can be reduced and maintenance saved, making glass fibers potentially much cheaper in the long run. "In-depth fibre life cycle cost analysis can be highly useful for policy-makers, as it gives them an overall sense of the financial cost implications for the different types of fibre they may choose and this can help them make long term, strategic investment decisions in large network infrastructure.
Choosing Fiber Optic Cable for Internet & Networks
Matching Cable Type to Application Needs
A single mode cable will significantly enhance performance, yet optimal performance always depends upon your network type and application. It is important to assess the needs in each individual use case — whether that be for residential internet applications or for massive data centers. Deciding the answer using factors such as the speed, distance and bandwidth of these environments is difficult as these environments can be very different from each other. For example, single mode fibers are generally chosen for long haul because of their lower signal attenuation and multimode fibers are applied in short distance hight-speed transmissions like those between buildings in a metropolitan area network, or within a data center.
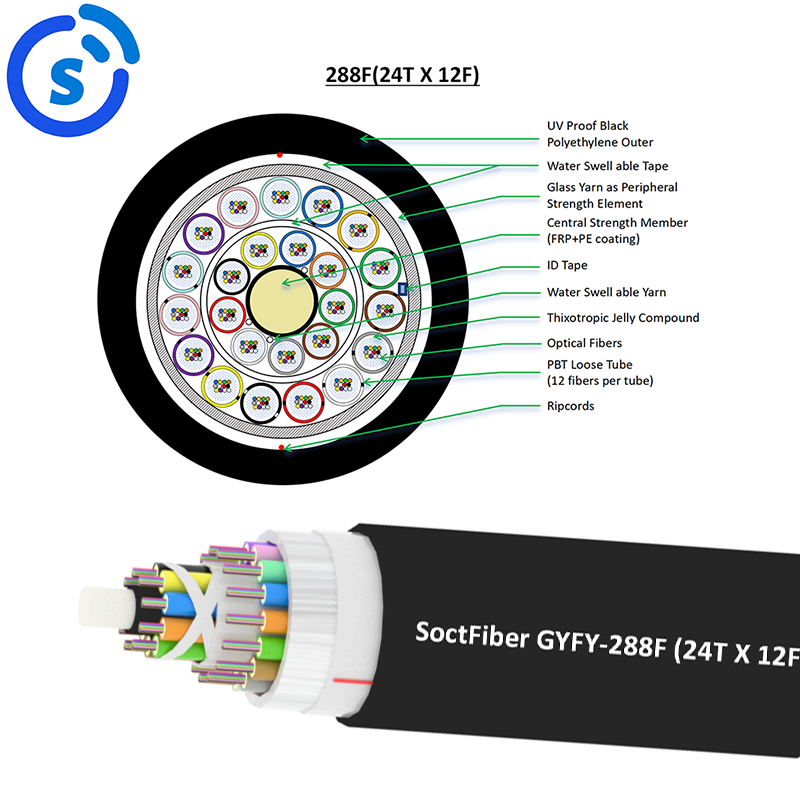
Future-Proofing with Fiber Optic Upgrades
Upgrading to fiber optic is an intelligent way to re-envision the network infrastructure by future-proofing it for new technologies and applications. Fiber optic equipment are noted for interoperability and flexibility, providing easy adjustment in bandwidth and ensuring a smooth expansion in data transmission capability in a timely manner. With industry forecasts to consider, this implies the demand for fiber optics should continue to rise as more and more businesses move toward high-speed, data-driven work. Through the addition of high-performing fiber optic cabling, businesses can benefit from a strong and versatile network infrastructure and a secure future.
Environmental Factors in Outdoor Installations
Selecting the Best Outdoor Fiber Optic Cable The selection of outdoor fiber optic cable is based on the environmental condition the cable will experience, such as temperature and UV light exposure. Specialty cables, with burn jackets, moisture-resistant features, etc, can often make a huge difference in the performance and longevity of an installation in harsh environments. Environmental technicians advise for thorough inspection of the installation sites to determine the best fiber optic options. Taking these factors into account, drastically reduces future issues and results in a solid reliable network implementation.
FAQ
What is the transmission distance capability of single-mode fiber optic cables?
Single-mode fiber optic cables can support transmission distances of over 40 kilometers.
Which environments are best suited for multimode fiber optic cables?
Multimode fiber optic cables are optimal for short-distance data transmission, particularly within office buildings, campuses, and data centers.
What are the cost benefits of using plastic optical fibers?
Plastic optical fibers offer cost benefits due to their lower installation expenses compared to traditional glass fibers, making them suitable for short-range applications and smaller budgets.
How do environmental factors affect fiber optic cable installations?
Environmental factors like temperature variations and UV exposure can impact fiber optic cable performance, requiring specialized cable types for outdoor installations to ensure reliability.

