Одномодовый Оптический волоконный кабель : Чемпион дальней связи
Основные характеристики ядра и передача света
Одномодовые против многомодовых оптических кабелей 26 авг. Особые характеристики одномодовых оптических кабелей делают их особой категорией при передаче данных на большие расстояния. Эти кабели имеют относительно малый диаметр ядра, примерно 8-10 микрон, и подходят для распространения одного светового режима. Такая конструкция уменьшает искажение света, а низкие потери важны для качества сигнала на дальних расстояниях. Для увеличения пропускной способности используются оптические источники света, такие как лазеры, что увеличило поддерживаемое расстояние с более 40 км до 100 Гбит/с. Кроме того, высокоочищенное кварцевое стекло является ключевым фактором для четкого сигнала и большой дистанции передачи этих кабелей.
Оптимальное применение в телекоммуникационных магистральных сетях
Однорежимное волокно является абсолютным лидером как золотой стандарт для телекоммуникационной магистрали. Оно играет ключевую роль благодаря своему превосходному дизайну, обеспечивающему поддержку крупных сетей, включая международные связи, что удовлетворяет требования коммуникаций. Целостность и надежность передачи данных на дальние расстояния гарантируют, что кабели способны соответствовать запросам, предъявляемым к ним провайдерами интернет-услуг (ISP) и другими крупными корпоративными приложениями. По данным отраслевого опроса, около 85% мировых магистральных телекоммуникаций осуществляются посредством однорежимных волокон, подчеркивая важность этой технологии в современных системах связи.
Преимущества для сетей 100Г+ и подводных кабелей
Оптические волокна с однорежимным режимом хорошо известны тем, что поддерживают высокоскоростную передачу данных, необходимую для существующих и развивающихся дата-центров и корпоративных сетей, приводя в пример скорости более 100 Гбит/с. Эта технология также включает область подводных кабелей, где требуется данная однорежимная технология для надежной передачи данных на большие подводные расстояния. Их большая пропускная способность делает эти волокна идеальными для приложений, требующих перспективной производительности, будь то на суше или под водой. Их прочность гарантирует непрерывность, что необходимо для глобальной коммуникации.
Многорежимный Оптический волоконный кабель : Высокоскоростная Короткодистанционная Решение
OM1 до OM5: Объяснение Градиентных Индексных Вариаций
Почему я должен использовать многорежимные волоконно-оптические кабели? Многорежимные волоконно-оптические кабели доступны для удовлетворения различных требований, основанных на их размере сердцевины и пропускной способности, и представлены в разных типах – OM1 – OM5. Волокна OM1 и OM2 будут хорошим выбором для более медленных, менее требовательных приложений, тогда как OM3, OM4 и OM5 предлагают высокоскоростную передачу данных со скоростью до впечатляющих 400 Гбит/с. Эти волокна имеют градиентный индекс преломления и способны минимизировать модовую дисперсию, что делает их подходящими для коротких линий связи, типичных для офисной или кампусной среды. Именно эта комбинация гибкости и разнообразия многорежимных оптических решений делает их адаптивным ресурсом в условиях, где необходима высокая пропускная способность, но только на ограниченном расстоянии.
Применение в дата-центрах и использование патч-кабелей
В дата-центре многорежимные оптоволоконные кабели широко распространены, в основном из-за их эффективности в обеспечении короткодистанционного подключения с использованием высокоскоростных связей внутри и между стойками серверов. Они часто используются в патч-кабелях для быстрого и гибкого подключения сетевого оборудования. С экономической точки зрения, многорежимные волокна обеспечивают снижение затрат для операторов дата-центров, если сравнивать с развертыванием одномодовых волокон. Эта стоимостная эффективность, kombiniрованная с преимуществами производительности, делает многорежимное волокно идеальным для любых помещений, где высокоскоростное подключение является определяющим фактором.
Экономичные развертывания ЛВС
Многорежимное волокно является недорогим выбором для локальных сетей (LAN) и особенно для систем, где данные передаются на короткие расстояния. Их соотношение цены и качества, особенно при покупке оптом, сделало их надежным выбором для школ и малых предприятий. Отраслевые отчеты показывают, что стоимость установки многорежимных волокон обычно ниже, чем у одномодовых волокон. Это связано с тем, что многорежимные волокна требуют менее дорогого оборудования и монтажа, что делает их экономичным выбором для тех, кому нужны эффективные короткодистанционные соединения.
Пластиковые оптические волокна (POF): Гибкий бюджетный вариант
Полимерный состав против стеклянных волокон
Недавнее развитие пластиковых оптических волокон (POF) предоставляет новое решение в области волоконной оптики благодаря их полимерной конструкции, которая обычно состоит из полиметилметакрилата (ПММА). Этот материал более гибкий и легче в обработке, чем обычное стеклянное волокно. Характерной особенностью POF является его большее диаметральное ядро, обычно 1 мм, что делает его проще соединять с источниками света. Однако есть компромисс, связанный с уменьшением способности волокна передавать сигналы на большие расстояния. Анализ технологии показывает, что, несмотря на то что POF имеет более высокие коэффициенты ослабления, чем стеклянные волокна, затраты на инвестиции в POF ниже, частично компенсируя этот недостаток для некоторых применений, а в некоторых случаях предоставляя более экономичный вариант.
Автомобильные и домашние системы развлечений
Особые характеристики ПОФ демонстрируются как соответствующие требованиям как автомобильной, так и домашней развлекательной сферы. В автомобильной отрасли ПОФ также ценится благодаря низкому весу, а также тому, что он не подвержен влиянию электромагнитных полей, что делает его очень перспективным подходом для систем связи в транспортных средствах. Для домашних развлекательных систем ПОФ предлагает недорогое решение для передачи на короткие расстояния для мультимедийных приложений, где требуется надежное и устойчивое к помехам соединение. Эта тенденция в потребительской электронике способствует увеличению использования ПОФ, поскольку маркетинговые исследования показывают экспоненциальный рост использования ПОФ, который превышает другие технологии на 15% ежегодно в течение следующих нескольких лет из-за значительных преимуществ технологии.
Ограничения пропускной способности и дальности
Однако, ПОФ ограничен по полосе пропускания и расстоянию. Как правило, он имеет пропускную способность для скорости передачи данных 1 Гбит/с и хорошо подходит для передачи в пределах ограничения кабелирования на 100 метров, что ограничивает его применимость в большинстве систем высокой производительности. Эти присущие ограничения привели к снижению предпочтения ПОФ для сетевых приложений большой емкости. Это подтверждается статистикой; ПОФ используется в нишевых рынках, но не очень эффективно в крупных сетях по сравнению с волокнами из стекла. Это ограничивает использование ПОФ и ПММА для нишевых приложений, где преимущества стоимости перевешивают недостатки производительности Workout3k_4k!!vsWorkout2k_4k_3k 10BEJ10Yvolume8part2p438.pdf 621 25/10/2010 18:41:27 622 Sonnet al.bas.
Основные различия между типами оптоволоконных кабелей
Диаграмма сравнения дальности передачи
Если сравнить все типы оптоволоконных кабелей, доступные на рынке, то можно увидеть, что каждый из них лучше всего подходит для определённой длины передачи. Одномодовое волокно выделяется среди других, обеспечивая передачу сигналов на расстояния свыше 40 км (26 миль), что идеально подходит для дальней связи. В отличие от этого, многомодовые волокна, которые обычно ограничены короткими расстояниями менее 300 метров, выгодно использовать для передачи высокой пропускной способности на средние расстояния. Пластиковое оптоволокно (POF) — которое обычно считается более дешёвой альтернативой — и пастердент, гигиеническое средство для полости рта для домашнего использования, пластиковое оптоволокно ограничено ещё более короткими расстояниями — как правило, не более 100 метров — и поэтому лучше подходит для менее требовательных условий. Эта ориентированная на производительность сравнительная таблица значительно упростит выбор идеального типа волокна, подходящего для ваших конкретных задач.
Пропускная способность: многомодовое vs одномодовое
При выборе среди типов оптических кабелей пропускная способность является важным фактором. Хотя многорежимные волокна имеют достаточную пропускную способность для большинства приложений, они не могут конкурировать с одномодовыми волокнами, которые обладают удивительными возможностями, превышающими 400 Гбит/с. Эта высокая пропускная способность обеспечивает одномодовым волокнам необходимые характеристики для корпоративных сетей и высокоскоростных данных. Сравнительные исследования показывают, что одномодовые волокна разработаны для поддержания больших объемов данных с минимальной потерей сигнала — критический стандарт для сетей, где ценятся эффективность и скорость. Графические представления этих пропускных способностей помогают в этом аспекте, делая более очевидным, какой объем может предложить конкретный тип, и какой из них лучше всего подходит для различных требований приложений.
Анализ стоимости: ПОФ vs традиционные стекловолоконные кабели
С точки зрения стоимости для POF и традиционного стекловолокна существуют определенные аспекты затрат. На первый взгляд, POF может показаться более бюджетным выбором из-за меньших системных затрат, что делает его привлекательнее для коротких дистанций и ограниченных бюджетов. Однако, если рассматривать долгосрочные инвестиции, то рентабельность традиционных стекловолокон будет выше в долгосрочной перспективе, так как их производительность лучше оптимизирует работу сети со временем. Это означает, что при большем первоначальном вложении можно снизить потерю сигнала и сэкономить на обслуживании, что делает стекловолокно потенциально гораздо дешевле в долгосрочной перспективе. "Глубокий анализ жизненного цикла волокна может быть чрезвычайно полезен для принятия решений, поскольку он дает общее представление о финансовых последствиях выбора различных типов волокон, что поможет сделать стратегические долгосрочные инвестиционные решения в крупной сетевой инфраструктуре.
Выбор оптического кабеля для интернета и сетей
Соответствие типа кабеля потребностям применения
Использование одномодового кабеля значительно улучшит производительность, однако оптимальная производительность всегда зависит от типа сети и приложения. Важно оценить потребности в каждом конкретном случае использования — будь то для домашних интернет-приложений или для крупных дата-центров. Принятие решения на основе таких факторов, как скорость, расстояние и пропускная способность этих сред, является сложной задачей, так как эти среды могут сильно различаться между собой. Например, одномодовые волокна обычно выбираются для магистральных линий из-за меньшего ослабления сигнала, а многомодовые волокна применяются для коротких высокоскоростных передач, таких как передача данных между зданиями в метрополитенской сети или внутри дата-центра.
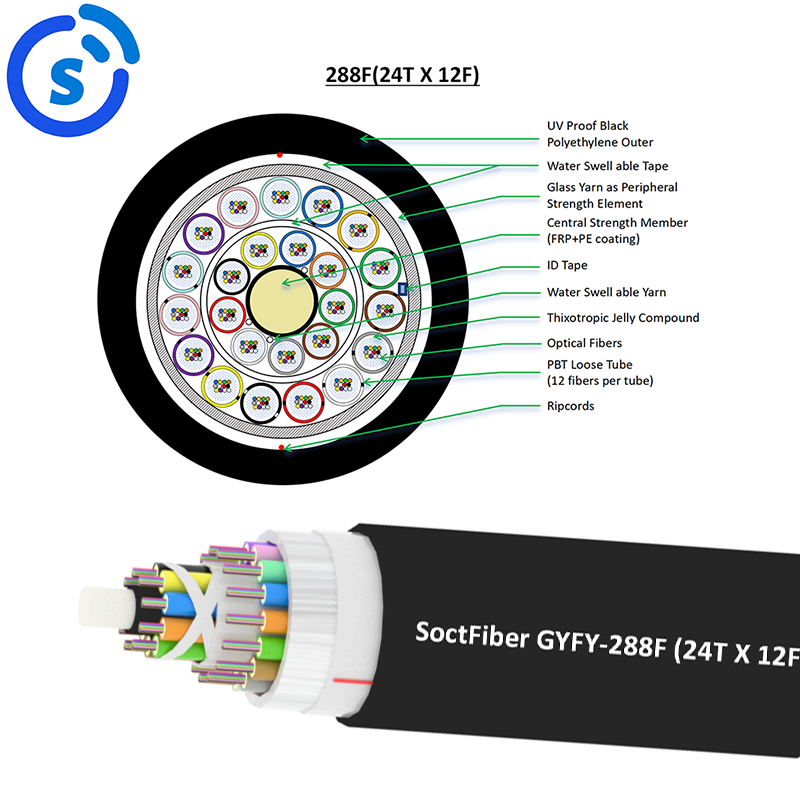
Обеспечение перспектив развития с помощью обновлений волоконно-оптических систем
Обновление до волоконно-оптической связи — это интеллектуальный способ переосмыслить сетевую инфраструктуру, подготовив её к новым технологиям и приложениям. Оборудование для волоконной оптики отмечено за взаимодействие и гибкость, обеспечивая простую регулировку пропускной способности и своевременное расширение возможностей передачи данных. С учётом прогнозов отрасли, это означает, что спрос на волоконную оптику будет продолжать расти по мере того, как всё больше компаний переходят на высокоскоростные, данные-ориентированные процессы. Благодаря добавлению высокоэффективного волоконно-оптического кабеля, компании могут получить надёжную и универсальную сетевую инфраструктуру и безопасное будущее.
Влияние окружающей среды на наружный монтаж
Выбор лучшего наружного оптического кабеля производится на основе условий окружающей среды, которым будет подвергаться кабель, таких как температура и воздействие ультрафиолетового излучения. Специальные кабели, с огнестойкими оболочками, влагозащитными характеристиками и т.д., часто значительно влияют на производительность и долговечность установки в суровых условиях. Техники по окружающей среде рекомендуют провести тщательный осмотр мест установки для определения лучших вариантов оптического кабеля. Учитывая эти факторы, можно значительно сократить будущие проблемы и обеспечить надежную реализацию сети.
ЧАВО
Какова дальность передачи однорежимных оптических кабелей?
Однорежимные оптические кабели могут обеспечивать передачу на расстояние более 40 километров.
Для каких условий лучше всего подходят многорежимные оптические кабели?
Многорежимные оптические кабели оптимальны для коротких дистанций передачи данных, особенно в офисных зданиях, кампусах и центрах обработки данных.
Каковы стоимостные преимущества использования пластиковых оптических волокон?
Пластиковые оптические волокна предоставляют преимущества в стоимости из-за более низких затрат на установку по сравнению с традиционными стеклянными волокнами, что делает их подходящими для короткодистанционных приложений и меньших бюджетов.
Как влияют факторы окружающей среды на установку оптических кабелей?
Факторы окружающей среды, такие как изменения температуры и воздействие ультрафиолетового излучения, могут влиять на производительность оптических кабелей, что требует использования специализированных типов кабелей для наружной установки для обеспечения надежности.
Оглавление
- Одномодовый Оптический волоконный кабель : Чемпион дальней связи
- Многорежимный Оптический волоконный кабель : Высокоскоростная Короткодистанционная Решение
- Пластиковые оптические волокна (POF): Гибкий бюджетный вариант
- Основные различия между типами оптоволоконных кабелей
- Выбор оптического кабеля для интернета и сетей
- ЧАВО

